(by Arturo Veneruso, Innovation Manager, GDPR expert and IT contract lawyer and member of the AIDR Observatory for the Digitization of the Environment and Energy)
From the cogency of Regulation (EU) 2016/679 which took place on 25 May 2018, the sanctions imposed by Government Bodies revealed the weaknesses of public and private organizations in relations with the so-called "interested parties", generally represented by consumers of products and services by the employees, or by the resources, to which the utmost attention must be paid, the first as they represent the basis for the increase of the GDP of each country, and the second, as functional for the organization for the production of provision of services.
These sanctions should be analyzed by all organizations to understand the areas that must necessarily be improved to follow an adequate behavior, in operational processes and in the relationship with technology.
In this sense, it would be appropriate to analyze the aforementioned sanctions from different areas, not only from the point of view of the typical themes of the European regulation sanctioned by the related articles, but also from the point of view of the organizational areas and its management aspects.
The following graphs show the percentage trend of the economic values and volumes of the sanctions relative to the European Community and Italy.
The community reality
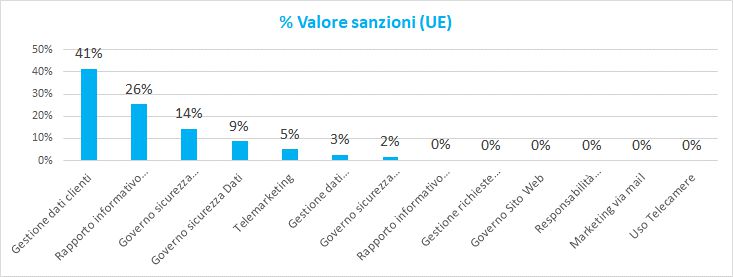
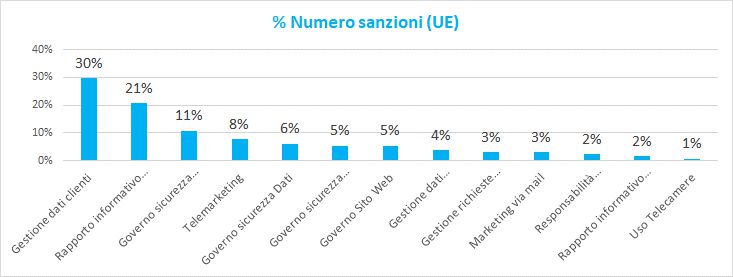
As can be seen in the European Community, the causes of sanctions are mainly linked to:
- Management of customer data with the presence of communications of personal data to irrelevant recipients
- Information relationship with customers with incomplete presentation of the information and inadequate consent management
- Security government Infrastructure with deficiencies in combating hackers or malicious software
The market areas most involved in the sanctions belong to the "Social", "Public Administration", "telecommunications", clothing, "tourism", "air transport" and "e-commerce" sectors.
The Italian reality
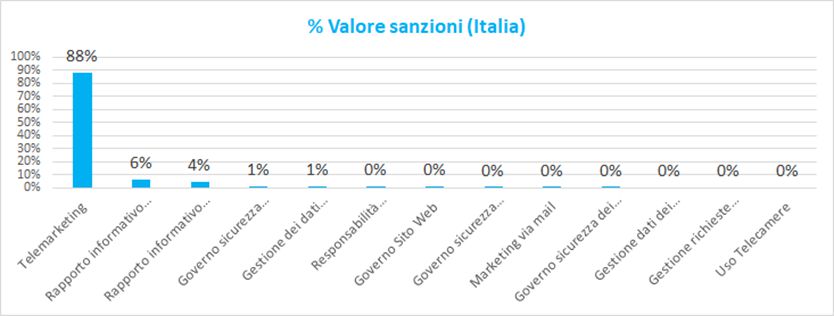
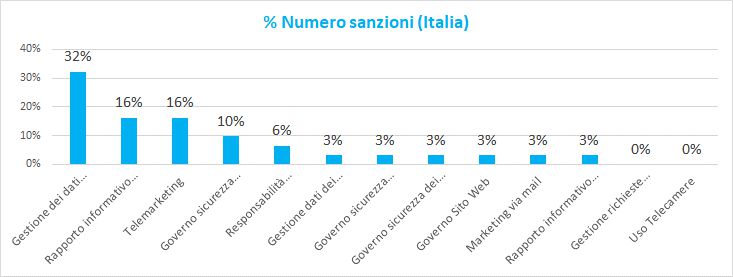
As can be seen in Italy the causes of the sanctions are mainly linked to:
- Telemarketing with invasive telephone commercial actions
- Management of customer data with the presence of communications of personal data to irrelevant recipients
- Information relationship with customers and employees with incomplete presentation of the information to employees and inadequate management of their consent
- Government security Infrastructure with deficiencies in the fight against hackers or malicious software
The market areas most involved in the sanctions belong to the "Telecommunications" and "Energy" sectors
From this analysis it can be understood how common areas for improvement exist in the European Community and in Italy and how, in our country, peculiar characteristics emerge relating, for example, to invasive commercial actions.
